计算机开机I/O控制卡输出瞬变
1.现象
用户反映在使用PCI-1230的I/O控制卡时,如果先给机台上电(常用规格为24V),再按下计算机的启动开关后,I/O控制卡的输出端口控制的外设(电磁阀,继电器)会有瞬间的变化(指示灯闪烁一下或气阀突然动作一下, 输出的位号不定)。
2.原因分析
计算机在上电时,主板会提供复位信号(RST#,低有效)到PCI设备,I/O控制卡的硬件设计会保证在复位信号有效期间使DO输出处于截止状态(电流无法通过); 复位信号长度与主板有关,常见的不小于100ms; 下图是PCI规范里面的复位时序:
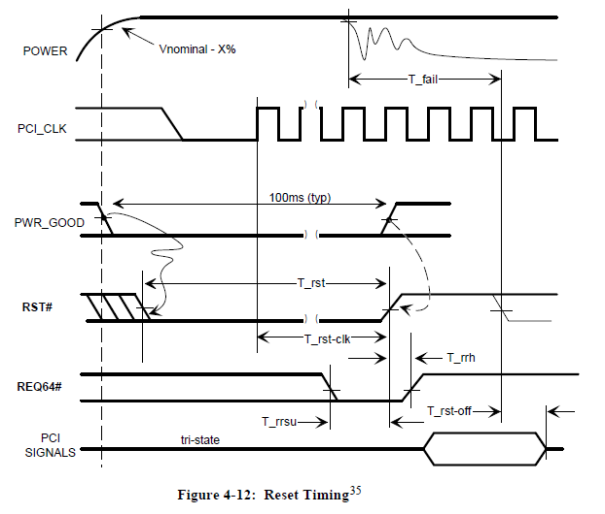
计算机在上电后,会执行BIOS程序,BIOS程序会通过读写一定范围的I/O空间来检测即插即用(Plug and Play)外围设备,包括主板内置的设备与用户另外增加的设备,比如数据采集卡,然后把相关的配置信息保存在CMOS芯片中提供给操作系统使用,之后才启动操作系统。
I/O控制卡输出瞬变,是BIOS程序在检测即插即用(Plug and Play)外围设备期间对I/O空间的读写造成的。
受影响的产品范围:PCI-1230, PCI-1232, PCI-1234,PCI-9014, PCI-9016等使用了PCI I/O空间(I/O Space)进行地址译码的设计。
3.解决方法
1) BIOS设置启用PnP OS
在计算机开机时,持续按住“Delete”键,进入BIOS设置界面,然后进入“Advanced”下面的“PCI / PnP”,点击回车键,即“Enter”键,选择“YES”后保存设置,再退出系统。如下图所示:
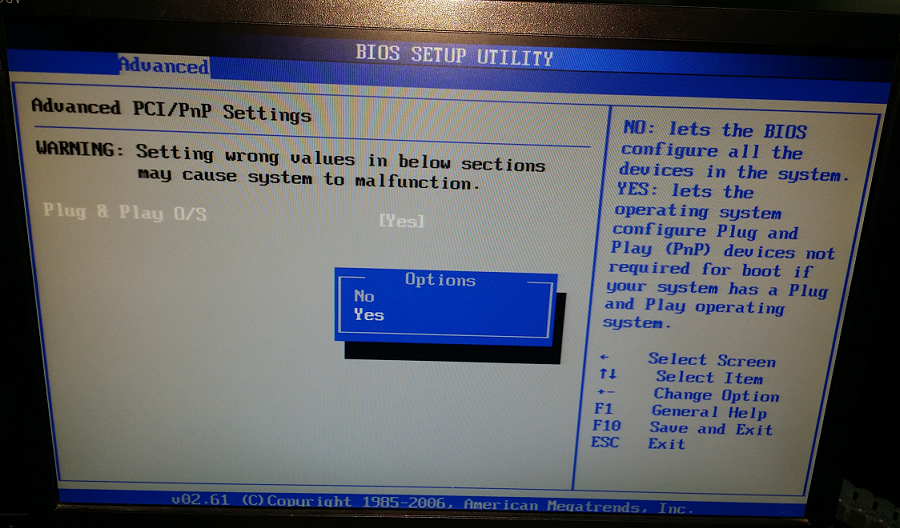
如上图的右边描述,这样设置的目的是在计算机启动时,BIOS只检测和设置与系统引导相关的即插即用硬件设备,其它的硬件设备由操作系统来配置; 这样保证了I/O控制卡在BIOS启动时不被检测和设置、I/O控制卡的DO端口就不会有瞬间信号输出。
2) 使用PCI Express接口控制卡
PCI Express接口的控制卡在设计时,全部使用存储器控件(Memory Space)进行地址译码,不会存在该问题。
3. 关于PnP OS
Setting the plug and play BIOS option (PNP OS) in CMOS Setup
When you start your
computer, the basic input/output system (BIOS) checks (among other things) the
system-specific settings that are stored in the complementary metal-oxide
semiconductor (CMOS) chip. You can modify these settings as the system changes.
To change the CMOS settings, you must enter CMOS
Setup by pressing a specific key or a combination of keys during the initial
startup sequence. For example, press DEL or CTRL+ALT+ESC during the startup.
(The specific key combination that you press is typically indicated during
startup as "Press
After you have entered Setup, windows that
display various options and settings appear. Some of these options are
standard, while others are specific to the BIOS manufacturer.
One of the CMOS settings is the PNP OS option. This setting tells BIOS how
many devices to configure at startup. The table in "More Information"
shows the effect of this option on the configuration of the motherboard
devices.
The original intent for designing this option
was to give Microsoft Windows versions 95 and 98 more freedom to adjust
hardware configurations. By default, these operating systems would never move a
device configured at startup for fear of breaking a DOS driver. Later versions
of Windows also typically leave BIOS-configured hardware alone, even if the
BIOS placed the hardware in a less than optimal configuration. This is because
moving such hardware frequently exposes latent bugs in the BIOS.
|
Setting |
Description |
|
PNP OS |
The BIOS configures only critical devices (for example, video, hard-disk, and key- Board). NOTE: In this mode, neither the BIOS nor Windows configures the motherboard devices at startup. Therefore, for these earlier computers, you must set PNP OS to No. |
|
PNP OS |
The BIOS configures critical devices and all motherboard devices under the assumption that Windows cannot. |
|
Former (legacy) |
The PNP OS option is irrelevant. Windows (only Windows versions 98, Millennium Edition, 2000 and XP) uses the Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) BIOS interface to configure motherboard devices and retrieve system information. NOTE: Although a system does have an ACPI BIOS, ACPI might have been disabled by Windows because of a bug in the ACPI BIOS. In this case, Windows will fall back to PNP BIOS and APM BIOS in read-only mode. Therefore, for any computer with a buggy ACPI BIOS, set PNP OS to No. |
资料来源:
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/321779/en-us



 首页
首页